6 Additional resources
6.1 Interactive networks
6.1.1 visNetwork
#install.packages('visNetwork')
library(visNetwork)
edges_visnet <- edges_1mode
colnames(edges_visnet)[c(1,2)] <- c('from', 'to')
nodes_visnet <- nodes_1mode
colnames(nodes_visnet)[2] <- 'label'
visNetwork(nodes_visnet, edges_visnet, width="100%", height="400px")6.1.2 networkD3
#install.packages('networkD3')
library(networkD3)
nodesd3 <- nodes_1mode[1]
nodesd3$zero_id <- 0:(nrow(nodesd3)-1)
edgesd3 <- edges_1mode
edgesd3 <- dplyr::left_join(edgesd3, nodesd3, by = c('from_org_id' = 'id'))
colnames(edgesd3)[7] <- 'from_zero_id'
edgesd3 <- dplyr::left_join(edgesd3, nodesd3, by = c('to_org_id' = 'id'))
colnames(edgesd3)[8] <- 'to_zero_id'
nodesd3$name <- nodes_1mode$name
forceNetwork(Links = edgesd3, Nodes = nodesd3,
Source="from_zero_id", Target="to_zero_id",
NodeID = "name", Group = 1, linkWidth = 1,
linkColour = "#afafaf", fontSize=12, zoom=T,
opacity = 0.8, charge=-300,
width = 600, height = 400)6.2 Useful tutorials
- Katya Ognyanova’s Network Visualization tutorials from PolNet have always been a great starting point for features across several packages
6.3 Other plotting packages
There are several plotting packages out there, some of them work with different network objects and requiring different knowledge. Excellent overviews of some of them are provided in this post by Katya Ognyanova. I won’t need to repeat these, but it is worth seeing the basic representation and understanding how igraph vs. network objects look differently in them, by default.
6.3.1 plot()
Base R plotting works with network and igraph objects, though their defaults for each object are different.
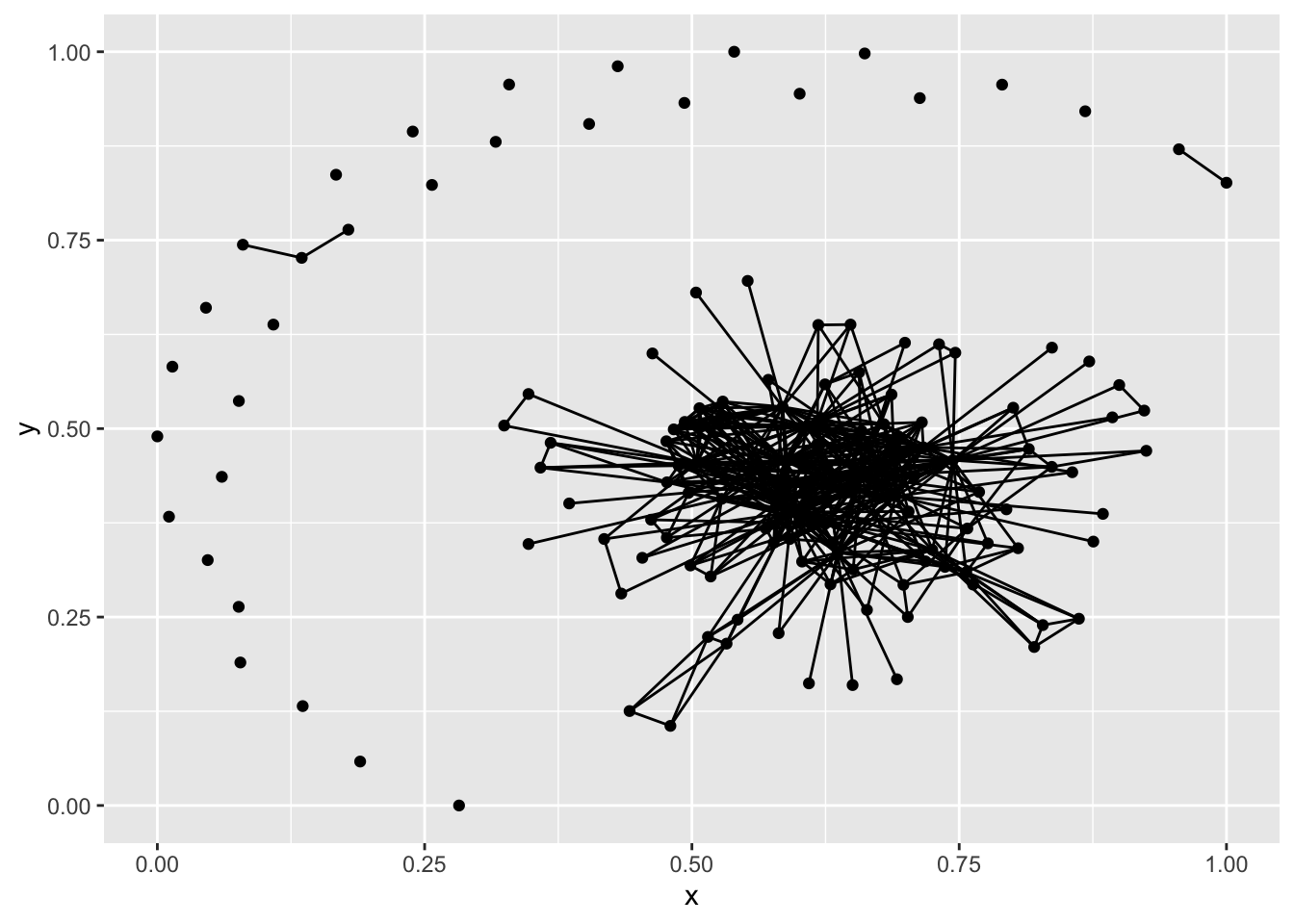
plot(net1)
plot(g1)

6.3.2 GGally::ggnet2()
The ggnet2 function is also dynamic, but despite being housed as part of the GGally extension of the ggplot2 series it seems to function more like a base R plot. For this function, igraph and network objects look the same.
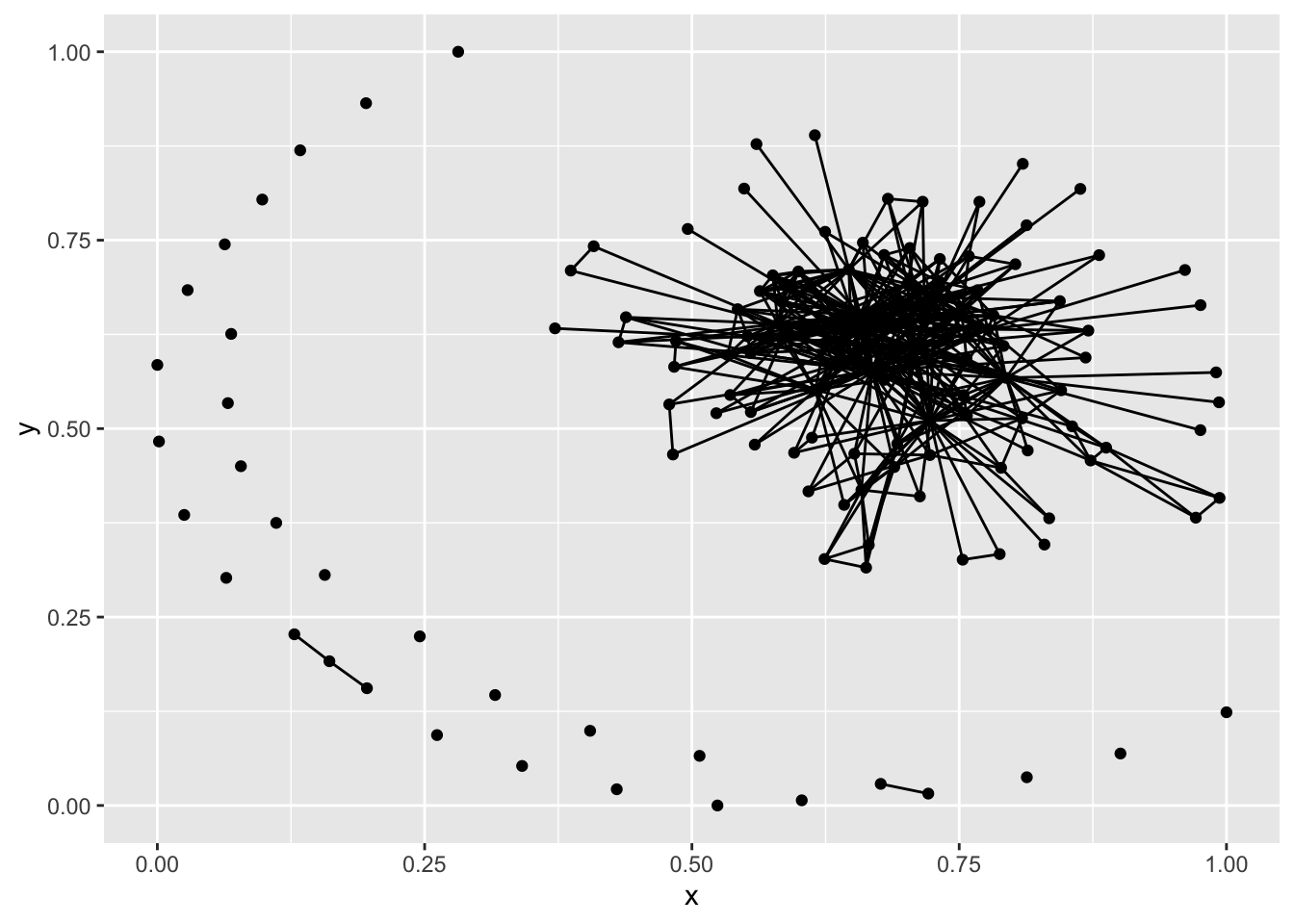
GGally::ggnet2(net1)
GGally::ggnet2(g1)
6.3.3 ggnetwork::ggnetwork()
Very similar to ggraph and also an extension of the ggplot family is the ggnetwork function. This function integrates directly with ggplot2 and specifies the default coordinates of ggraph, but otherwise operates quite similarly. For this function, igraph and network objects look the same.
library(ggplot2)
library(ggnetwork)
ggplot(net1, aes(x = x, y = y, xend = xend, yend = yend)) +
geom_nodes() +
geom_edges()
ggplot(g1, aes(x = x, y = y, xend = xend, yend = yend)) +
geom_nodes() +
geom_edges()